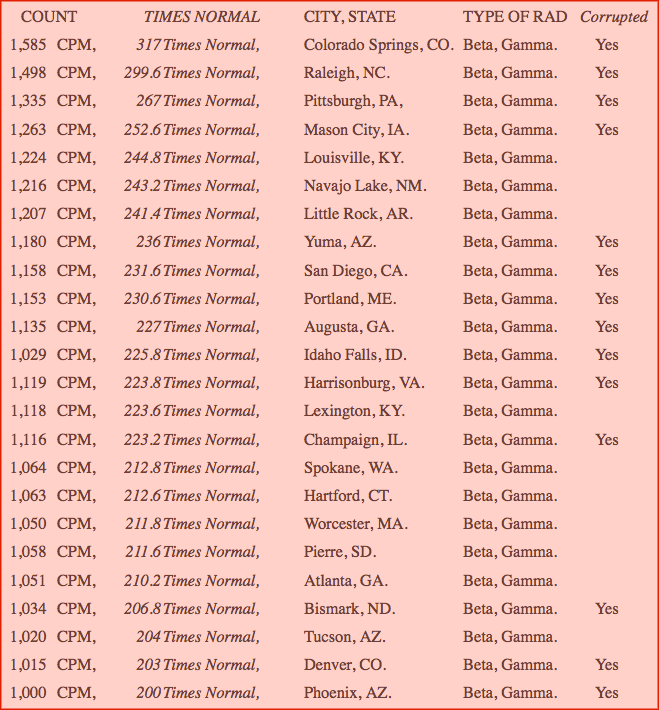
Radiation Cpm Chart
Radiation Cpm Chart - Web do you have to know which radiation type are you measuring with a geiger counter to correctly estimate the equivalent dose rate? It is the number of atoms in a given quantity of radioactive material that are detected to have decayed in one minute. If you have your geiger counter calibrated to cs137, which most are, 1 millirad per hour would equate to 1,200 cpm on your counter. At the same time, 1 microsievert per hour would equate to 120 cpm on the reading. Web a place to log background radiation, display charts and map, build, chat and create. Web counts per minute (cpm) is a measure of radioactivity. Web dosage rates, total doses and exposure guidelines (8760 minutes in one year, 60 cpm = 0.038 mr/hr = 0.38 µs/hr) Web cpm (counts per minute) 3 60 secs dpm = becquerel (bq) 4 becquerel = 1 disintegration/second (dps) 5 curie = ×3.7 10 10 becquerels 6 curie = ×2.22 10 12 dpm = 2 1 i d 1 = 2 2 i d 2 i1 = radiation field at distance d1 i2 = radiation field at distance d2 7 inverse square law (isl) af = 2n a = af = final activity ai = initial activity n= t t * t. 1,200 cpm on the meter (for cs137) is about 1 mr/hr (millirad per hour). These numbers will establish a baseline so that you will be able to determine if the background radiation has changed, or to detect trace amounts of radioactive materials. Use the dashboard below to select the monitoring location. For this tube, multiply its cpm by 0.0057 to get the equivalent usv/hr radiation level. At the same time, 1 microsievert per hour would equate to 120 cpm on the reading. Interest to scientists, managers, and the general public. Figure 1 illustrates the more common types of ionizing radiation. You can see there there's a lot of randomness in the data. Radmon.org is for experimenters, enthusiasts and background radiation monitoring. Web do you have to know which radiation type are you measuring with a geiger counter to correctly estimate the equivalent dose rate? Web use the radiation dose calculator to estimate your yearly dose from sources of ionizing radiation. View a pdf version of the radiation terms and units infographic here. Figure 1 illustrates the more common types of ionizing radiation. Web the highest and lowest cpm count will establish your minimum and maximum cpm. Web here's a graph which shows counts per minute, cpm, measured by the above geiger counter sitting in my stanford office. Use nuclear medicine and radiation therapy technologists or others familiar with the use of radiation. Interest to scientists, managers, and the general public. If you have your geiger counter calibrated to cs137, which most are, 1 millirad per hour would equate to 1,200 cpm on your counter. These numbers will establish a baseline so that you will be able to determine if the background radiation has changed, or to detect trace amounts of radioactive materials.. Web counts per minute (abbreviated to cpm) is a measure of the detection rate of ionization events per minute. In the table above the common units and si units in each row are not equivalent in value, i.e., 1 curie does not equal 1 becquerel, but they both measure the same parameter. For this tube, multiply its cpm by 0.0057. Interest to scientists, managers, and the general public. Web dosage rates, total doses and exposure guidelines (8760 minutes in one year, 60 cpm = 0.038 mr/hr = 0.38 µs/hr) Web what are normal radiation levels cpm and what are dangerous ones? At the same time, 1 microsievert per hour would equate to 120 cpm on the reading. Web radnet has. 1 sievert = 100 rem. Use nuclear medicine and radiation therapy technologists or others familiar with the use of radiation detection instruments ; Web this manual provides an orientation on ionizing radiation, and describes the radiation safety policies and procedures we have implemented to ensure a safe environment for our patients and students, the public, and ourselves. Web a place. Web this manual provides an orientation on ionizing radiation, and describes the radiation safety policies and procedures we have implemented to ensure a safe environment for our patients and students, the public, and ourselves. Web most geiger counters are calibrated to cs137 (cesium), a radioactive isotope. Disintegrations per minute (dpm) is also a measure of radioactivity. Goal is < 2. Web this manual provides an orientation on ionizing radiation, and describes the radiation safety policies and procedures we have implemented to ensure a safe environment for our patients and students, the public, and ourselves. If you have your geiger counter calibrated to cs137, which most are, 1 millirad per hour would equate to 1,200 cpm on your counter. Web dosage. Web this manual provides an orientation on ionizing radiation, and describes the radiation safety policies and procedures we have implemented to ensure a safe environment for our patients and students, the public, and ourselves. Figure 1 illustrates the more common types of ionizing radiation. Disintegrations per minute (dpm) is also a measure of radioactivity. Web what are normal radiation levels. It is the number of atoms in a given quantity of radioactive material that are detected to have decayed in one minute. Presence of radioactive substances in a volume or on a surface where they are unwanted and undesired (air, water, internally in the body, etc.) Counts are only manifested in the reading of the measuring instrument, and are not. Web use the radiation dose calculator to estimate your yearly dose from sources of ionizing radiation. Web radioactivity cpm conversion tool using the radioactivity cpm conversion tool click on the steps below for detailed instructions about each page of the cpm conversion tool. Web most geiger counters are calibrated to cs137 (cesium), a radioactive isotope. For this tube, multiply its. Web counts per minute (abbreviated to cpm) is a measure of the detection rate of ionization events per minute. For this tube, multiply its cpm by 0.0057 to get the equivalent usv/hr radiation level. It is the number of atoms in a given quantity of radioactive material that are detected to have decayed in one minute. View a pdf version of the radiation terms and units infographic here. Web a place to log background radiation, display charts and map, build, chat and create. Web counts per minute (cpm) is a measure of radioactivity. Counts are only manifested in the reading of the measuring instrument, and are not an absolute measure of the strength of the source of radiation. If you have your geiger counter calibrated to cs137, which most are, 1 millirad per hour would equate to 1,200 cpm on your counter. Web a geiger counter produces a “tick” or click when significant radiation is observed. Web cpm (counts per minute) 3 60 secs dpm = becquerel (bq) 4 becquerel = 1 disintegration/second (dps) 5 curie = ×3.7 10 10 becquerels 6 curie = ×2.22 10 12 dpm = 2 1 i d 1 = 2 2 i d 2 i1 = radiation field at distance d1 i2 = radiation field at distance d2 7 inverse square law (isl) af = 2n a = af = final activity ai = initial activity n= t t * t. Goal is < 2 times background radiation reading Web most geiger counters are calibrated to cs137 (cesium), a radioactive isotope. Use the dashboard below to select the monitoring location. 120 cpm on the meter (for cs137) is about 1 usv/hr (microsievert per hour). Web what are normal radiation levels cpm and what are dangerous ones? Web radnet has 140 radiation air monitors in 50 states and runs 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.⚛ Your Radiation 61, June 1118, 2016 🌎 ⚛ ⚛ ⚛ Leuren Moret Global
Radioactive Safety Chart
The Hemlock Tea Room and Ladies' Emporium RADIATION TOPS TENS OF
Nuke Pro Waves of Radiation Passing Over USA
Nuke Pro Geiger Counter Interpretation Simplified
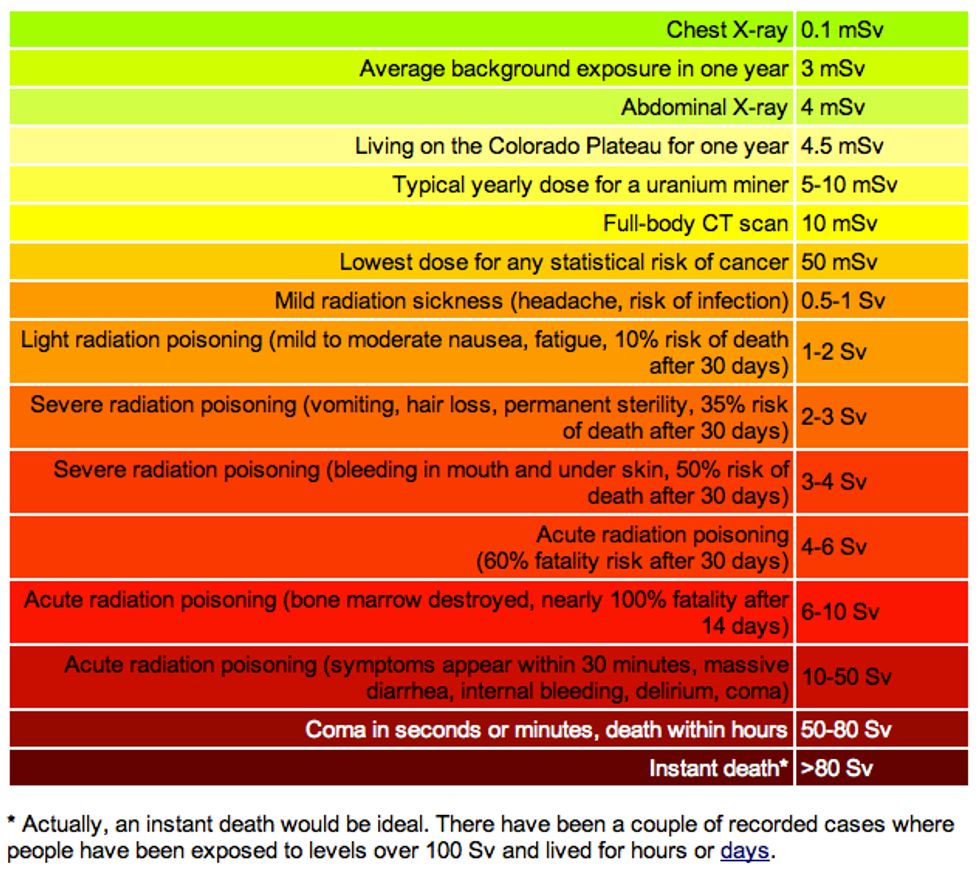
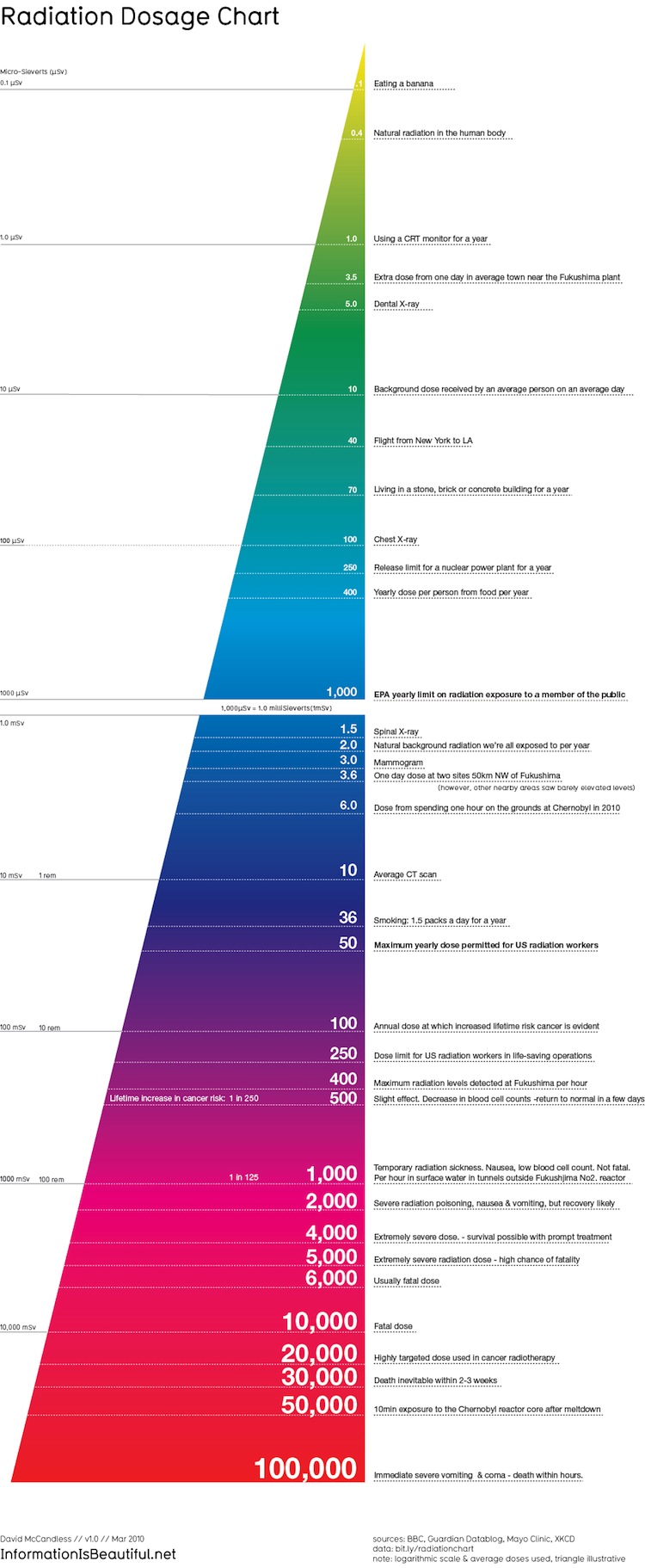
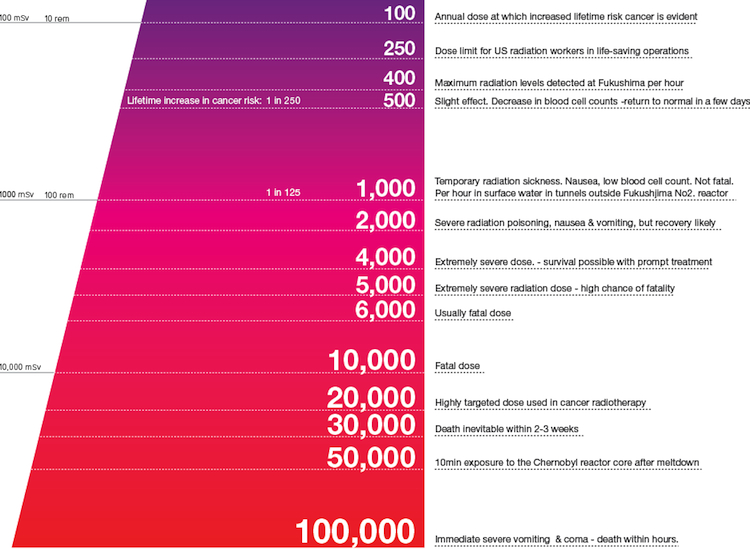
A Chart to Better Understand Radiation Levels and Their Effects on
Infographic of the Day The Best Radiation Chart We’ve Seen So Far
Nuke Pro Geiger Counter Interpretation Simplified
Radioactive Safety Chart
Infographic of the Day The Best Radiation Chart We’ve Seen So Far
Web In General, The Radiation Intensity Is Usually Measured In Counts Per Minute (Cpm) Or Counts Per Second (Cps), Which Expresses A Rate Of Counts Per Unit Time Registered By A Radiation Monitoring Instrument.
1,200 Cpm On The Meter (For Cs137) Is About 1 Mr/Hr (Millirad Per Hour).
Web Here's A Graph Which Shows Counts Per Minute, Cpm, Measured By The Above Geiger Counter Sitting In My Stanford Office.
You Can Send Background Radiation Readings From A Wide Range Of Geiger Counters, Home Built Or Kit Built Or Some Commercial Counters.
Related Post: