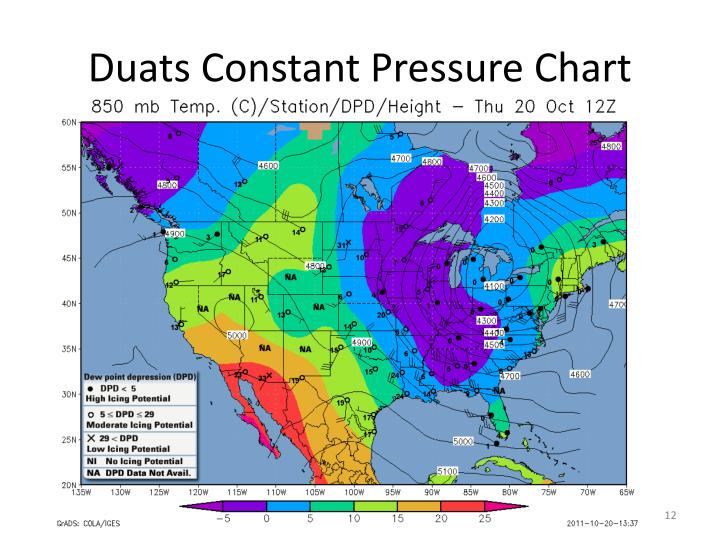
Constant Pressure Chart
Constant Pressure Chart - Alternate term for isobaric chart; Upper air charts and analyzed maps. Why use a constant pressure chart? The map on the left is constructed from data collected at a pressure value of 500 mb (about half of. Web typical levels of constant pressure charts with each showing different aspects of the atmosphere. Web thickness is the measurement of the distance (in meters) between any two constant pressure surfaces. An air pressure of 700 millibars is commonly equivalent. It shows areas of maximum vorticity,. Web you could draw a topographic map of the sloping constant pressure surface by drawing contour lines of altitude or height. Both at the surface and in the upper atmosphere, meteorologist constantly. Upper air charts and analyzed maps. 700 mb is considered by many to be the top of the lower atmosphere. First, take a look at this post that. Web constant pressure charts: Why use a constant pressure chart? The l and h on this map represent low and high. Web thickness is the measurement of the distance (in meters) between any two constant pressure surfaces. Web an air pressure of 300 millibars is said to occur near 30,000 feet (9,100 meters) in elevation, but the height ranges from near 27,000 to 32,000 feet (8,200 to. For example, a 500 mb chart. Find out how these features help forecast the. Both at the surface and in the upper atmosphere, meteorologist constantly. Web thickness is the measurement of the distance (in meters) between any two constant pressure surfaces. Web constant pressure charts: Web during winter, the jet core is located generally closer to 300 millibars since the air is more cold and dense in the vicinity of the jet stream during. Find out how these features help forecast the. The l and h on this map represent low and high. 700 mb is considered by many to be the top of the lower atmosphere. The images below represent 500mb height forecasts utilizing the latest operational models and/or gfs ensemble guidance. Both at the surface and in the upper atmosphere, meteorologist constantly. Web a constant pressure chart by itself doesn't provide any useful data for flight planning. Web learn how to interpret the 500 mb level chart, which shows the height, vorticity, humidity and wind barbs of the atmosphere. 700 mb is considered by many to be the top of the lower atmosphere. As it shows a height of a given pressure. One of the most common thickness charts used in. Web thickness is the measurement of the distance (in meters) between any two constant pressure surfaces. Why use a constant pressure chart? Web a constant pressure chart by itself doesn't provide any useful data for flight planning. First, take a look at this post that. Web a constant pressure chart by itself doesn't provide any useful data for flight planning. An air pressure of 700 millibars is commonly equivalent. Both at the surface and in the upper atmosphere, meteorologist constantly. The images below represent 500mb height forecasts utilizing the latest operational models and/or gfs ensemble guidance. Find out how these features help forecast the. Web typical levels of constant pressure charts, with each showing different aspects of the atmosphere. Upper air charts and analyzed maps. For example, a 500 mb chart. Web you could draw a topographic map of the sloping constant pressure surface by drawing contour lines of altitude or height. Find out how these features help forecast the. Web these charts are prepared for several mandatory pressure levels twice daily (0000 z and 1200 z) from the temperature, humidity and wind data provided by the operational. Web you could draw a topographic map of the sloping constant pressure surface by drawing contour lines of altitude or height. Web typical levels of constant pressure charts, with each showing different. The images below represent 500mb height forecasts utilizing the latest operational models and/or gfs ensemble guidance. Web thickness is the measurement of the distance (in meters) between any two constant pressure surfaces. The l and h on this map represent low and high. Both at the surface and in the upper atmosphere, meteorologist constantly. As it shows a height of. Web during winter, the jet core is located generally closer to 300 millibars since the air is more cold and dense in the vicinity of the jet stream during the cool season. Web shown below is the 700 mb constant pressure chart from the gfs model (recommended). As it shows a height of a given pressure level, you can make. First, take a look at this post that. Web typical levels of constant pressure charts, with each showing different aspects of the atmosphere. The images below represent 500mb height forecasts utilizing the latest operational models and/or gfs ensemble guidance. Web a constant pressure chart by itself doesn't provide any useful data for flight planning. Both at the surface and in. The images below represent 500mb height forecasts utilizing the latest operational models and/or gfs ensemble guidance. Why use a constant pressure chart? Web you could draw a topographic map of the sloping constant pressure surface by drawing contour lines of altitude or height. Web typical levels of constant pressure charts, with each showing different aspects of the atmosphere. 700 mb is considered by many to be the top of the lower atmosphere. It shows areas of maximum vorticity,. Web during winter, the jet core is located generally closer to 300 millibars since the air is more cold and dense in the vicinity of the jet stream during the cool season. Both at the surface and in the upper atmosphere, meteorologist constantly. First, take a look at this post that. Web shown below is the 700 mb constant pressure chart from the gfs model (recommended). Web these charts are prepared for several mandatory pressure levels twice daily (0000 z and 1200 z) from the temperature, humidity and wind data provided by the operational. Web thickness is the measurement of the distance (in meters) between any two constant pressure surfaces. Find out how these features help forecast the. Alternate term for isobaric chart; Upper air charts and analyzed maps. The map on the left is constructed from data collected at a pressure value of 500 mb (about half of.Constant pressure chart basics
Constant pressure chart basics
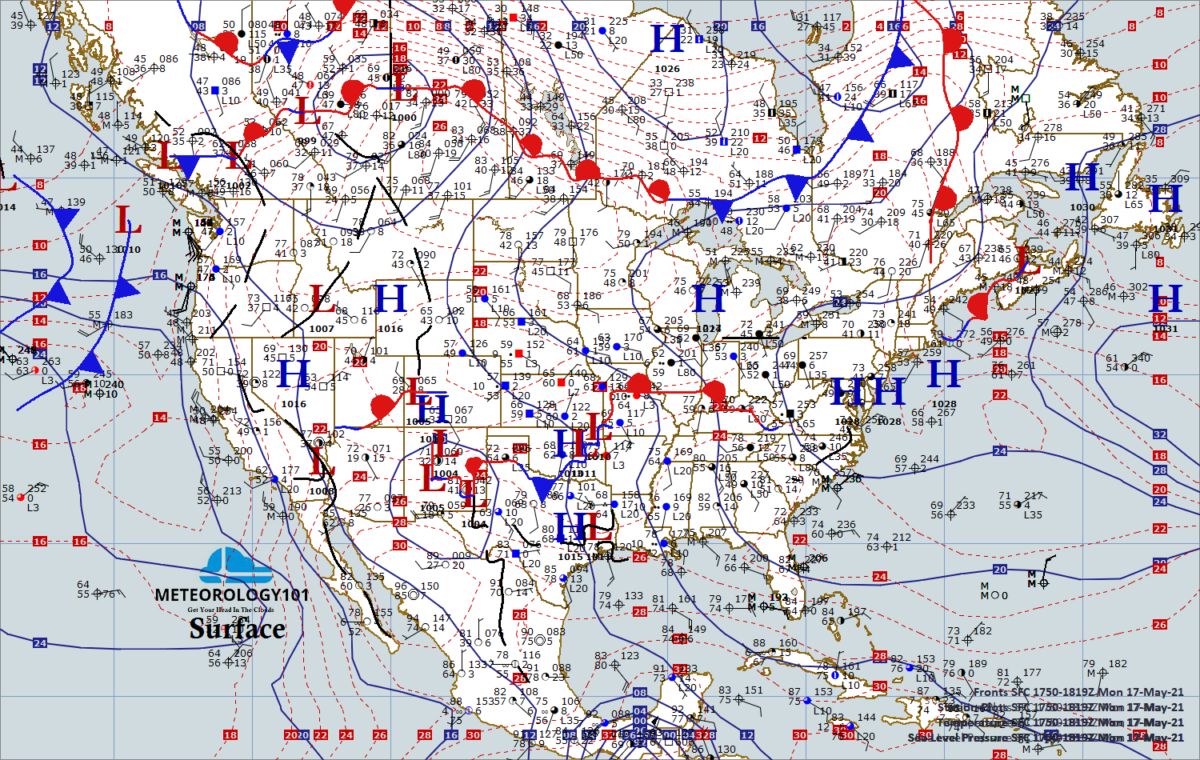
Surface & Upper Air Constant Pressure Charts Meteorology101
Surface & Upper Air Constant Pressure Charts Meteorology101
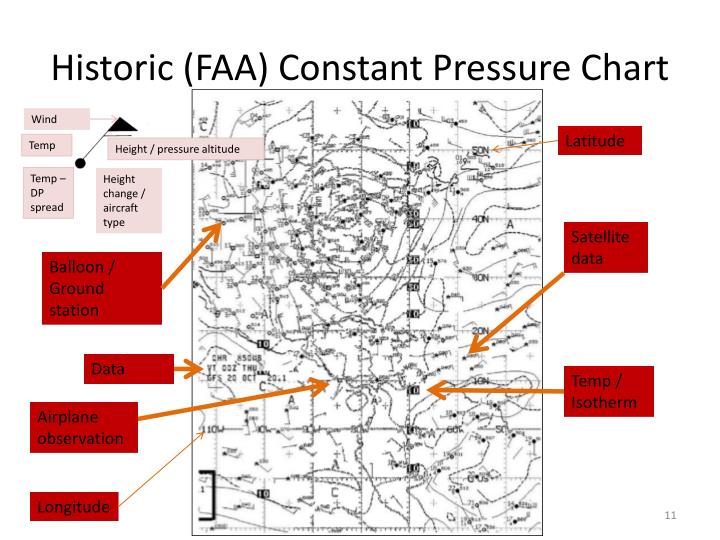
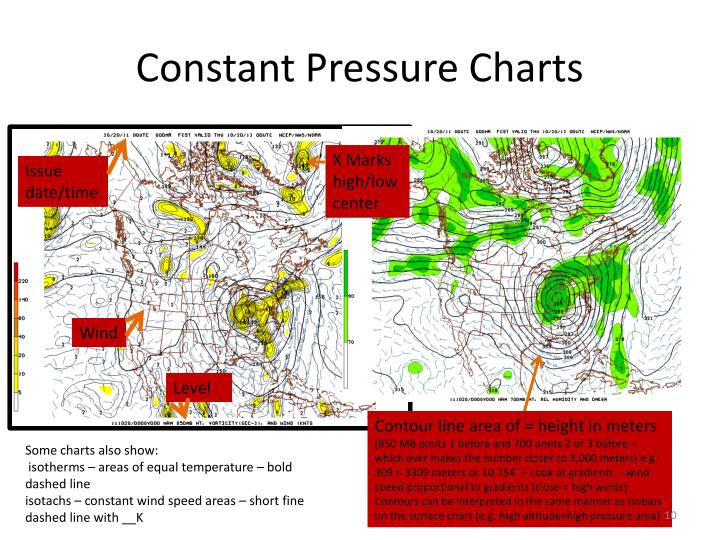
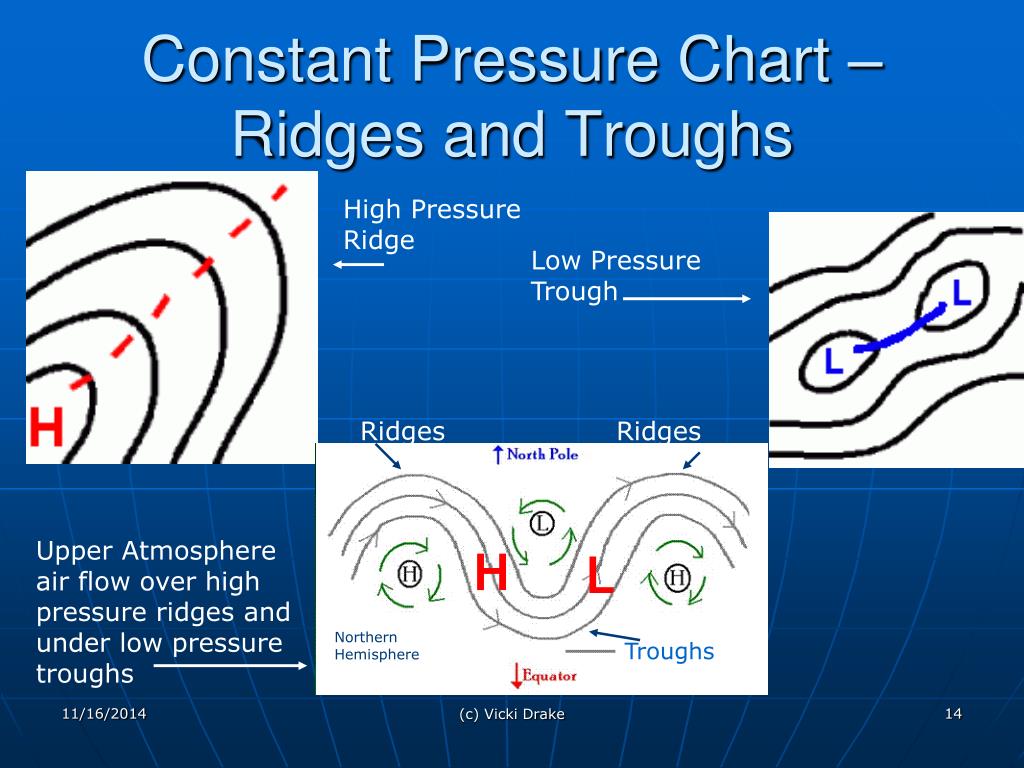
PPT Weather Charts PowerPoint Presentation ID5007142
PPT Weather Charts PowerPoint Presentation ID5007142
Weather Pressure Chart
PPT AIR PRESSURE AND WINDS PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Common Features of Constant Pressure Charts National Oceanic and
PPT Weather Charts PowerPoint Presentation ID5007142
A Weather Map Representing Conditions On A Surface Of Equal Atmospheric Pressure.
Web So From My Understanding, The Constant Pressure Chart Gives A 12 Hour Forecast Of Weather Conditions At Different Altitudes.
Web A Constant Pressure Chart By Itself Doesn't Provide Any Useful Data For Flight Planning.
Web Constant Pressure Charts:
Related Post: